Add a Startup sound when logging in or when machine starts up - Login Sound / Melody on Linux Desktop
I was looking a way to play a sound/melody when my machine boots. I found a potential solution here. But the "Start Up" application mentioned in the article was not available on my Gnome Shell installation. It tried various options from that web-page and ran the commands available in console / terminal. Results are as follows.
This solution did not work
opensuseleap@localhost:~> /usr/bin/canberra-gtk-play --id="desktop-login" --description="GNOME Login"
Failed to play sound: File or data not found
This solution worked
opensuseleap@localhost:~> paplay /usr/share/sounds/purple/login.wav
When i ran the above command in terminal i could hear a pleasant melody.
To Play sound when logging in
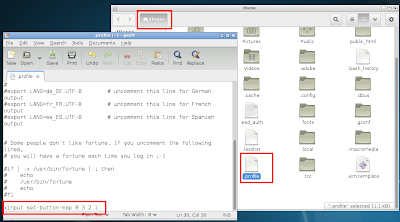
I added the above command to my ~.profile file and voila . I can now hear pleasant sound when i start my machine. To open the .profile file you can press ALT+F2 followed by typing in the text ~.profile and then pressing Enter/Return key. Usual location of .profile file is /home/<ReplaceWithUserName>/.profile
Open .profile file using Run Command Window Alt+F2
.profile file showing the paplay command to play login sound/melody
Note:- Solution tested on openSUSE Leap 15.2, GNOME SHELL VERSION 3.34.4