Razor-qt is desktop which a KDE-ish
- highly configurable,
- easy-to-use,
- light weight(low hardware requirements),
- fast desktop environment based on Qt.
Razor-qt cosists of various components:-
- Panel -you can add plugins, behave like GNOME 2.X applets
- Desktop with icons support
- Application launcher(razor-runner)
- Settings (Configuration center)
- Sessions
Razor-qt works with various WMs, but Openbox seems to be the preferred window manager.
Installation:-
I have openSUSE 12.3/ GNOME 3.6 installed, the following procedure was used to install Razor-qt.
Pre-installation:-
First i turned-off Autologin , created "new" user and used this new user for logging into Razor-qt. For details see User Management on GNOME 3.X
Installation using YaST
Add repo
Add the following additional repo using YaST:-
http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/X11:/QtDesktop/openSUSE_12.3/
Install Packages
Install the following packages using YaST Installer
- Base packages
- razorqt
- pavucontrol -simple GTK based "mixer" for PulseAudio
- Additional packages
- qtdesktop - Will pull in various "Must have" Qt applications :-
- juffed - Simple tabbed text editor
- nomacs - Lightweight image viewer
- qlipper - Lightweight clipboard history
- qterminal - Advanced terminal emulator
- quiterss - QuiteRSS - RSS/Atom aggregator
- qupzilla - Web browser based on WebKit core
- qxkb - Qt keyboard layout switcher
- qpdfview - Tabbed PDF Viewer
- screengrab - Screen grabber
- clementine - A cross-platform Music Player based on Amarok 1
- smplayer - Complete Frontend for MPlayer
- speedcrunch - A calculator with history display
- vlc - multimedia player for various audio and video formats
- qbittorrent - A Bittorrent Client built with C++ / Qt4
Installation using zypper
Add repo
open comman launcher(Alt+F2) and open terminal using command ("gnome-terminal") and run following command:-
sudo zypper ar -c -f -n 'QtDesktop_openSUSE_12.3' http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/X11:/QtDesktop/openSUSE_12.3/ QtDesktop_openSUSE_12.3
Install Packages
Run in the following command in terminal to install the desktop
sudo zypper in razorqt pavucontrol qtdesktop
Razor-qt Overview
At first time login, Razor-qt provides a dialogue box with a list of window managers and I chose Openbox
The default desktop looks conservative with a touch of gloss. The analog clock adds a nice touch to the desktop.
We see a traditional main menu (Alt+F1)
Lot of plugins / applets can be added to panel by right clicking on it. We can see Application Menu, Quick Launch, Task Manager, Colour Picker, Lock Tool, CPU Usage tool, Network Usage tool, Show Desktop tool etc.. added in the screenshot below
Each plugin on panel can be customised. Task Manager can be customised to make opened applications look like squares instead of rectangles.
Desktop icons / items can be added by creating launchers inside ~/Desktop folder by using commands like "gnome-desktop-item-edit 1.desktop"
Razor runner makes launching applications keyboard friendly (Alt+F2).
Razor Configuration Center
The Razor Settings applet / plugin on the panel is very useful in configuring the desktop. "Razor Session Configurator" can be used to make applications like Artha(Dictionary tool) to start along with the desktop.
To change themes we need to use both "Openbox Configuration Manager" as well as "Razor Appearance Configuration" .
"Razor Shortcut Configuration" can be used to create keyboard shortcuts to launch applications easily using keyboard.
Qt Applications
SpeedCrunch is a cool calculator which has lot of inbuilt formulae
qBittorrent makes a powerful torrent downloader. qpdfview is a cool lightweight pdf viewer with "tabs" support.
JuffEd is a good text editor and NoMacs does a good job as image viewer
QupZilla makes a wonderful webkit based browser and has variety of features like AdBlock, RSS reader, Cookie Manager and web inspector. It also has a good collection of inbuilt themes.
SMPlayer and VLC (Audio & Video players) play almost anything you throw at them.
To configure mouse settings from command line we can use an utility called "xinput". The manual for xinput defines it as a utility to list available input devices, query information about a device and change input device settings. i.e. xinput can be used to configure a variety of input devices like mouse, keyboard etc...
List Connected Devices
On a GNOME 3.x desktop we can open command launcher (Alt+F2) and then use the command "gnome-terminal" to open terminal.
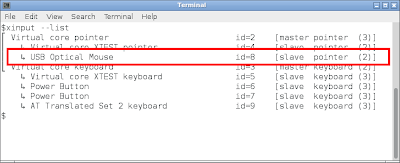
To list all the devices connected to a machine we can run the following command in terminal xinput --list. In the following screenshot you can find that an optical mouse is connected to the machine and assigned a "device id 8".
Enable and Disable the device
Sometimes we don't want mouse movement to bring up a machine from sleep. To disable the input device(mouse), we find the device id by listing all devices as shown above. After finding the device id of the mouse (8) we can run the following command in terminal to disable the mouse xinput --disable 8. Similarly to enable mouse again we can run the command xinput --enable 8. To make things more convenient we can set keyboard shortcuts for these commands as shown below
Switch mouse buttons from right handed to left handed
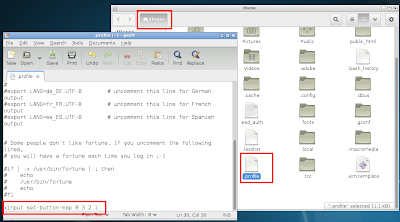
I for one use, "left handed" mouse settings . I find that on some "light weight" desktops, GUI based mouse settings are often not available which makes changing mouse settings a hassle. xinput comes to the rescue in these cases. To get the default mouse button mapping the following command can be used :- xinput get-button-map 8. To change the default mapping from right to left you can use the command xinput set-button-map 8 3 2 1. The following screenshot shows the demo.
The above setting made through terminal will last only for one login session but, we can "apply" this setting every time we login by plugging the relevant command into the ~/.profile file in "home" directory as shown below.
Dconf is
- low-level configuration system whose main purpose is to provide a backend to GSettings on GNOME 3.X desktops.
- dconf is a simple key-based configuration system. Keys exist in an unstructured database.
- dconf system can be considered as a kind of replacement for gconf system which was used in GNOME 2.X series desktop.
- dconf-editor is a Graphical Editor for Simple key-based configuration system which is dconf.
Install dconf Editor
Launch dconf Editor
- To launch dconf Editor open command launcher
(Alt+F2) and run command "dconf-editor".
- Alternatively you can press left "Win" key or
(Alt+F1) to open "Activities" and type "dconf" upon which you can see dconf Editor appearing grouped under "Applications".
dconf Editor Essentials
Find keys
The various keys can be found by invoking search settings from top panel and then plugging in appropriate "search string" as shown below
dconf Editor is a very useful configuration editing tool and the inner "workings" are as follows:-
- All the settings are categorised broadly under Schemas.
- All the Keys that logically belong together are grouped together under Schemas.
- The various key's values can be changed by double clicking on them and entering new values. To save new settings we need to press return key .
- To restore original values we can always use the "Set to default" button at the bottom of the tool.
dconf Editor Usage
The tool can be used for many purposes like:-
- Changing preferences/settings for many native GNOME applications settings. Example:- Get Totem working again after crash by changing schema
"org.gnome.totem"
- Perform some advanced settings which is sometimes not possible to do from even the applications. It is possible to reduce inbox refresh time to 30 seconds in Evolution. In this case it is accomplished by changing schema
"org.gnome.evolution.mail"
Evolution interface allows minimum refresh rate of 1 minute
dconf Editor allows reduction of refresh rate to 30 seconds.
- Change default directory where the screenshots are stored if "Print Screen" button is pressed. In this case schema that is modified is
"org.gnome.gnome-screenshot"
- We can change mouse button modifier (Modifier to use for modified window click actions) from <SUPER> or "Win" key to <ALT>. You can use "Alt" key and click on any open window to "drag" it around. The schema to be changed in this case is
"org.gnome.desktop.wm.preferences".
- It can serve as a replacement / alternative for
"gnome-tweak-tool" and "gnome-control-center". Most of the settings in Tweak tool are available / changed using dconf Editor.
- Change mouse from left to right click by editing the schema
"org.gnome.settings-daemon.peripherals.mouse" as shown below.